Type of Forces

Types of Forces in AS-Level Physics
At AS level, forces are categorized into different types based on how they act and their effects on objects. Here’s a closer look at key force types, including weight, normal contact force, frictional force, resistive force, and upthrust.
Force is the rate of the change in momentum.
1. Weight(W)
• Definition: The force due to gravity acting on an object’s mass.
• Formula: W = mg
Where is the mass of the object (in kg) and is the gravitational field strength ( 9.81 ms^-2 on Earth).
• Direction: Always acts vertically downward toward the center of the Earth.
2. Normal Contact Force
• Definition: The force exerted by a surface perpendicular to the object in contact with it.
• Direction: Acts perpendicular to the surface.
3. Frictional Force(f)
• Definition: The force that opposes the relative motion or attempted motion of two surfaces in contact.
• Formula:
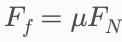
Where mu is the coefficient of friction (static or kinetic) and FN is the normal contact force.
• Direction: Opposes the direction of motion or attempted motion.
• Types:
• Static friction: Prevents motion from starting.
• Dynamic friction: Opposes motion of moving objects.
4. Resistive Force
• Definition: Forces that oppose motion through a medium (e.g., air, water).
• Types:
• Air Resistance (Viscous Drag by air): Opposes motion through the air; depends on speed, shape, and surface area.
• Viscous Drag by liquid: Opposes motion through liquids.
• Direction: Always acts opposite to the direction of motion.
5. Upthrust (Fu)
• Definition:Upthrust is caused by pressure difference on top and bottom surfaces
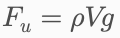
Where rho is the fluid density, V is the displaced volume, and g is gravitational field strength.
• Direction: Acts vertically upward.
• Example: A boat floating on water experiences an upthrust equal to its weight.
Summary of Directions
| Force | Direction |
|---|---|
| Weight | Vertically downward |
| Normal Contact | Perpendicular to the surface |
| Frictional | Opposite to the motion or attempted motion |
| Resistive | Opposite to the motion through a medium |
| Upthrust | Vertically upward |